
The significance of limiting global warming to a 1.5°C increase above pre-industrial levels is outlined in the Paris Agreement.
The innovative ‘Global temperature trend monitor’ application developed by Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) emphasises the urgency of climate change mitigation.
The Paris Agreement and the 1.5°C Target
Limiting global warming to 1.5˚C is agreed to under the Paris Agreement. The Paris Agreement’s primary goal is to limit the global temperature rise to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, and to pursue efforts to restrict the increase to 1.5°C.
Achieving the 1.5°C target is critical, as even a half-degree difference can have severe consequences for our planet.
Urgency of Limiting Temperature Increase
Global warming has already caused significant changes in human and natural systems. Limiting the temperature increase to 1.5°C can mitigate adverse effects and enable effective adaptation. Immediate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is crucial.
Experts project the 1.5°C limit could be reached between 2030 and the early 2050s without action. This rise could have far-reaching consequences, impacting ecosystems, agriculture, water resources, and vulnerable communities.
Global Temperature Trend
In the fight against climate change, knowledge is crucial. The Copernicus Climate Change Service offers a valuable resource – the ‘Global temperature trend monitor’ application. This tool allows anyone to monitor the current rate of global warming and assess the proximity to the critical 1.5°C limit if current trends persist. Visit the temperature trend application.
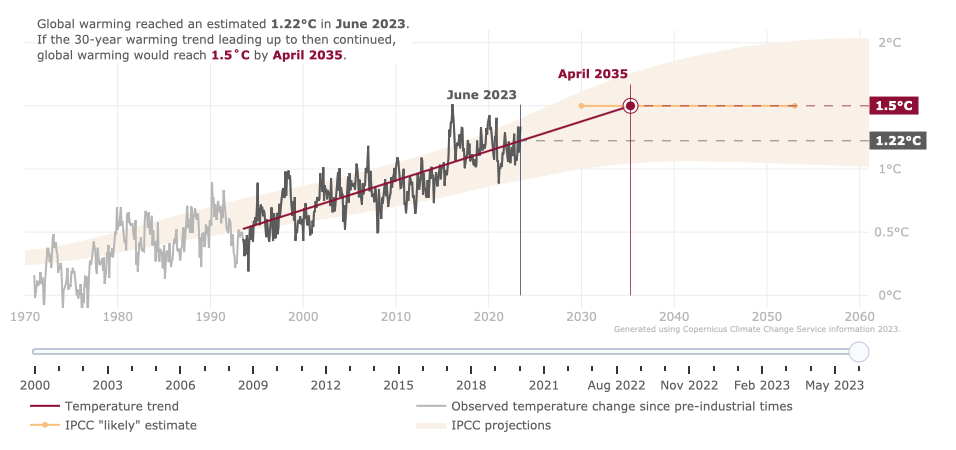
The application uses a sliding scale to visualise temperature changes from 2000 to the present day. A red line shows the 30-year average warming rate, projecting it into the future until it intersects with the 1.5°C limit. The 30-year average ensures stability amid short-term variations.
Future Projection
The ‘Global temperature trend monitor’ app does not provide concrete predictions but illustrates potential temperature changes if global warming rates continue. Climate change is complex, influenced by various factors, including natural variations and weather events, leading to uncertainties in future temperatures.
By raising awareness and leveraging scientific data, we can collaboratively work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for our planet. Together, let’s take decisive steps to address climate change and safeguard the well-being of current and future generations.
FAQ
What is the current rate of global warming towards the 1.5°C limit?
The current rate of global warming is accelerating towards the 1.5°C limit.
Is there a specific time frame for reaching the 1.5°C global warming threshold?
The time frame for reaching the 1.5°C global warming threshold is uncertain but projected within a few decades, between 2030 and the early 2050s.
What are the consequences if global warming exceeds the 1.5°C limit?
Exceeding the 1.5°C limit could have severe consequences for ecosystems, agriculture, water resources, and vulnerable communities.
What actions can we take to slow down the rate of warming and avoid reaching 1.5°C?
Immediate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is crucial. Take public transport, choose a low emissions car, carpool, buy a solar or gas energy efficient water heater, switch off your hot water system when you’re away. Read more about reducing your CO2 emissions.
How does limiting global warming to 1.5°C benefit ecosystems and vulnerable communities?
Limiting global warming to 1.5°C benefits ecosystems and enhances resilience for vulnerable communities.
Are there any recent updates or changes in projections that impact the timeline for reaching 1.5°C warming?
Ongoing efforts to improve climate models and updated data continually refine projections that impact the timeline for reaching 1.5°C warming.
Ready to reduce your carbon footprint?
Take action now! Calculate your carbon footprint using our Carbon Offset Calculator.


